|
|
Two
Kinds of Computer Graphics |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
There are two kinds of computer graphics -
raster (composed of pixels) and vector
(composed of paths). Raster images are more commonly
called bitmap images.
A bitmap image uses a grid of individual pixels where
each pixel can be a different color or shade. Bitmaps
are composed of pixels.
Vector graphics use mathematical relationships between
points and the paths connecting them to describe an
image. Vector graphics are
composed of paths.
The image to the left below is representative of a bitmap
and the image to the right is representative of a vector
graphic. They are shown at four times actual size to
exaggerate the fact that the edges of a bitmap become
jagged as it is scaled up:
Bitmap Image:
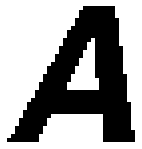 |
Vector Graphic:
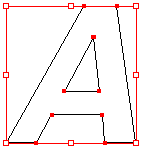 |
With Adobe® Systems' introduction of the PostScript®
page-description language computers could display fonts
and images using point-to-point math rather than by
pixels alone. The advantage to using a page-description
language such as PostScript becomes clear when you scale
an image up. The larger you display a bitmap, the more
jagged it appears, while a vector image remains smooth
at any size. That is why PostScript and TrueType®
fonts always appear smooth - they are vector-based.
The jagged appearance of bitmap images can be partially
overcome with the use of "anti-aliasing".
Anti-aliasing is the application of subtle transitions
in the pixels along the edges of images to minimize
the jagged effect (below left). A scalable vector image
will always appear smooth (below right):
Anti-Aliased Bitmap Image:
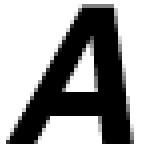 |
Smooth Vector Image:
 |
Bitmap images require higher resolutions and anti-aliasing
for a smooth appearance. Vector-based graphics on the
other hand are mathematically described and appear smooth
at any size or resolution.
Bitmaps are best used for photographs and images with
subtle shading. Graphics best suited for the vector
format are page layout, type, line art or illustrations.
Wherever possible use the vector format for all your
type, line art and illustrations and only use bitmaps
for photos or images with complex or non-uniform shading.
If the graphics application recognizes native vector
files such as those created by Deneba Canvas™ (a
filename with an extension of .CNV- for versions
6 and 7), Adobe Illustrator® (a filename with an
extension of .AI), CorelDRAW® (a filename with an
extension of .CDR), or Macromedia® FreeHand®
(a filename with an extension of .FH8 - for version
8), then use them first.
The EPS File Format
If the graphics application you are using cannot read
native vector files the next best thing would be to
save them as EPS (Encapsulated PostScript) files. These
are self-contained PostScript files which contain the
same mathematical descriptions as the vector files they
are made from. Even bitmaps can be saved in the EPS
file format. EPS files are supported by most all graphics
applications. It is the most portable format for this
reason. It is best to use EPS files for all line art
and illustrations because they can be reproduced at
any size or resolution and still display exactly as
they were drawn. Use them wherever native vector files
cannot be used.
A Little of Both In Today's Applications
Today's graphic artist has to master both skills -
image editing and illustration. In fact, Adobe Photoshop®
- an image editor - incorporates vector based paths
which can be exported as native vector files. Four of
the major illustration programs - Deneba Canvas, Adobe
Illustrator, CorelDRAW and Macromedia Freehand - allow
bitmaps to be embedded in the vector files they create.
I believe that the ideal page layout program of the
future would be primarily a vector-based application
which would create, import, display and print native
vector objects side by side with bitmaps. As computing
power becomes more affordable I believe this will happen.
Click
Here To Continue...
|